Myopia (commonly termed short-sightedness) Progression is a condition where the light rays focus in front of the retina. It happens when the cornea is excessively curved or the eye is too long, which prevents light from focusing on the retina. Distant objects appear blurred while near objects are clear.
What are the Factors that contribute to Myopia development?
– Genetic factors
– Environmental / Lifestyle factors
- Decrease in outdoor activity
- Increased usage in smartphones / near digital devices / near tasks
What are the Problems faced by Myopia?
Apart from the functional deficits when Myopia is uncorrected, it can affect
career choices as well. In very small percentages Myopia becomes
pathologic and is associated with an increased risk of Cataracts, Glaucoma, Retinal detachment or squint and maculopathy. Other problems faced by Myopia are:
-
Difficulty seeing objects at a distance: Myopia impairs vision, making it difficult to focus on faraway objects. As a result, it could be challenging to see traffic signs or see the board in a classroom.
-
Eye strain and fatigue: Myopic individuals frequently need to squint or strain their eyes in order to see effectively. Eye strain, headaches, and even neck and back pain may result from this.
-
Increased risk of eye diseases: A higher risk of major eye conditions such as glaucoma, cataracts, and retinal detachment is linked to high myopia.
-
Reduced quality of life: Daily tasks including driving, participating in sports, and socialising might be hampered by myopia. Also, it can have an impact on someone’s confidence and self-esteem, particularly in kids and young people.
- Dependence on corrective lenses: Myopic people frequently use corrective lenses like glasses or contact lenses to improve their vision. For some people, this may be uncomfortable, costly, and inconvenient.
What measures can prevent the onset and progression of Myopia?
It is well known that the common forms of childhood myopia are due to axial elongation (i.e a longer eyeball). The early intervention process aims at modifying this hence the potential for the progression of Myopia. While myopia can be corrected with glasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery, it is important to control its progression. Here are some expert tips from Zamindar Microsurgical Eye Centre on how to do just that.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Increased time spent outdoors—at least 2 hours of daylight exposure—is found to be helpful. Reduced time on smartphones, digital devices, or other near tasks has also been proven beneficial. Taking breaks from near work or reading, using good ambient lighting, and maintaining a reading distance of 20–30 cm are also preventive measures.
- Optical Treatment: Spectacle lenses and/or contact lenses are commonly used to manage myopia progression effectively.
- Pharmacological Treatment: Atropine 0.01% eye drops instilled nightly have shown 30–60% efficiency in slowing myopia progression in children over a two-year period. The drops should be tapered off gradually to avoid a rebound increase in myopia.
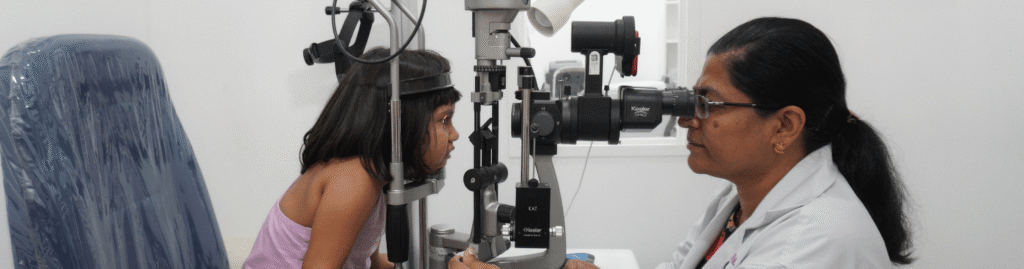
- Get Regular Eye Exams: Routine eye exams allow early detection and tracking of myopia progression. Eye doctors can prescribe corrective lenses and adjust prescriptions as needed.
- Spend Time Outdoors: Spending time outside has been linked to reduced myopia progression, particularly in younger individuals. Aim for at least two hours per day of outdoor activity.
- Practice Good Posture: Poor posture can contribute to eye strain and myopia progression. Sit up straight and position screens so the top is at or below eye level. Maintain a comfortable viewing distance.
- Eat a Healthy Diet: A nutrient-rich diet supports overall eye health. Include plenty of fruits and vegetables, especially those rich in vitamin A, such as carrots, spinach, and sweet potatoes.
You may manage your myopia and stop it from becoming worse by obtaining regular eye exams, cutting back on screen time, spending more time outdoors, practising good posture, utilising the right lighting, eating a balanced diet, and looking into myopia control treatments.













