Best Retina Specialist in Bangalore
Zamindar Microsurgical Eye Centre offers cutting-edge infrastructure and modern treatments for every retinal disease.
About Retina
The retina is a thin layer of tissue that lines the back of the eye on its inner aspect. It contains millions of light-sensitive cells (rods and cones) and other nerve cells that receive and organize visual information. The purpose of the retina is to receive light that the lens has focused, convert the light into neural signals, and send these signals on to the brain enabling us to see.
Various Retinal Conditions
There are a wide variety of retinal conditions and diseases. Here is a short list of the more common retina problems:
a. Diabetic Retinopathy
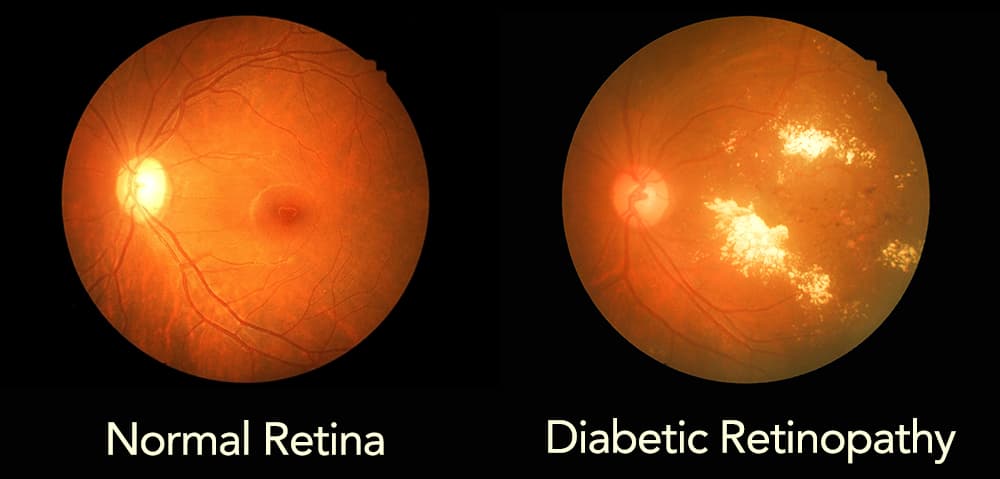
It is a serious complication of diabetes that affects the eye. It is caused by damage to the blood vessels of the retina.
The damaged blood vessels may leak fluids and fat into the retina. If this occurs in the central part of the retina or macula, edema develops. This is called diabetic maculopathy.
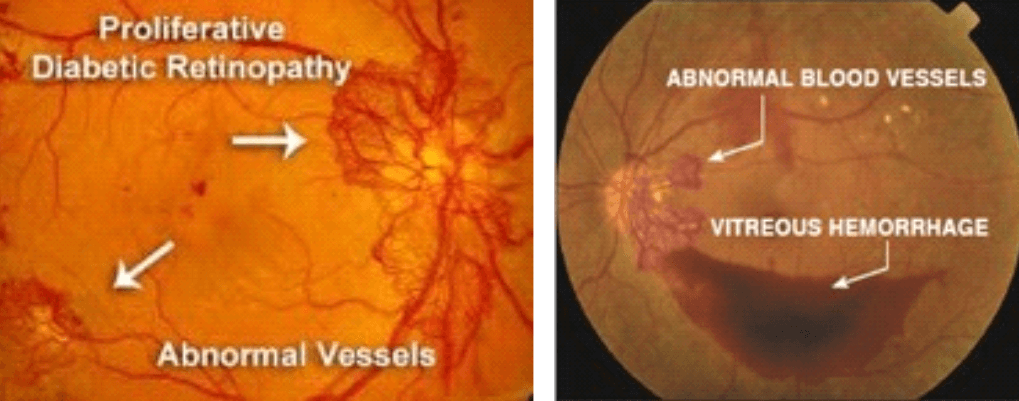
As the disease progresses, to improve blood circulation in the retina, new blood vessels may form on its surface. These fragile, abnormal blood vessels may bleed into the clear, jelly-like substance that fills the centre of the eye also called the vitreous. This is called vitreous hemorrhage.
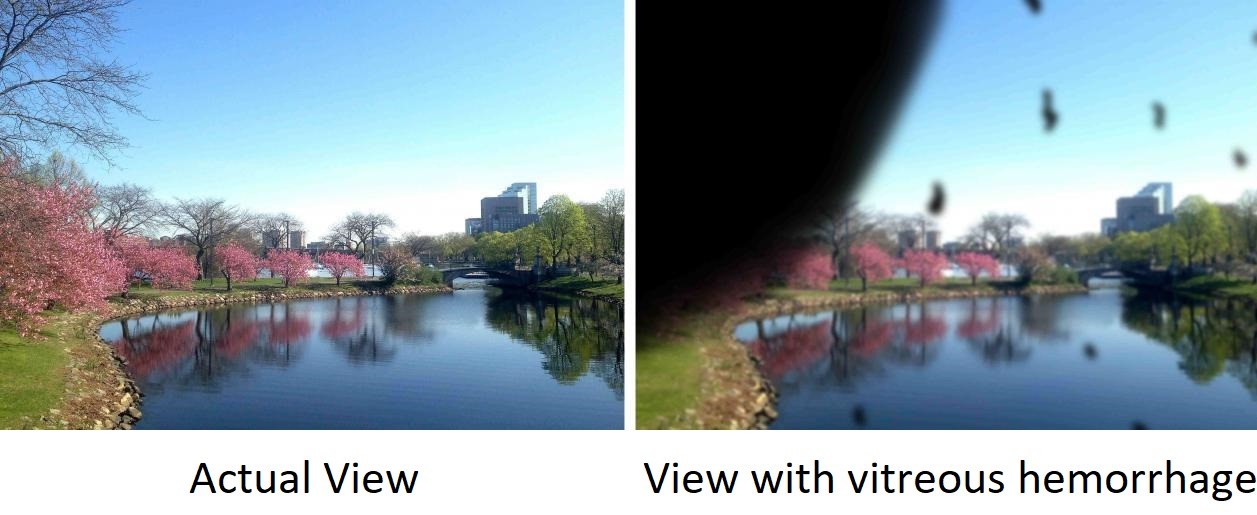

Vision may seem like this for patients with diabetic vitreous hemorrhage.
b. Macular Degeneration

Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a common cause of irreversible visual loss in individuals above the age of 50 years. The health of the macula determines our ability to read, recognize faces, drive, watch television, use a computer or phone, and perform any other visual task that requires us to see fine detail.
It occurs in two forms, dry or wet AMD. The less common wet AMD usually leads to more serious vision loss. In wet macular degeneration, abnormal blood vessels grow beneath the retina and leak blood and fluid. This leakage causes permanent damage to light-sensitive retinal cells or photoreceptors in the macula and creates a central blind spot in the affected person’s visual field.
c. Retinal Venous Occlusion
Diabetic Retinopathy is a complication of diabetes. It occurs when diabetes damages the tiny blood vessels inside the retina, the light sensitive area at the back of the eye.
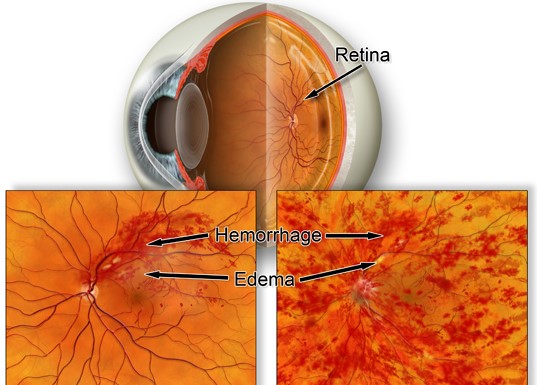
When a retinal vein that drains blood from the retina is blocked, it leads to bleeding and leakage of fluid from the blocked blood vessels.
d. Macular Edema
This is an accumulation of fluid at the macula, causing distortion and blurred central vision. Macular edema has several causes, including diabetes. In some cases, swelling of the macula can occur after cataract surgery.
e. Central Serous Retinopathy
This happens when fluid builds up under the central retina, causing distorted vision. Though the cause of central serous retinopathy often is unknown, it tends to affect men more frequently than women, and stress appears to be a major risk factor.
f. Hypertensive retinopathy
Chronic high blood pressure can damage the tiny blood vessels that nourish the retina, leading to significant vision problems.
g. Macular Hole
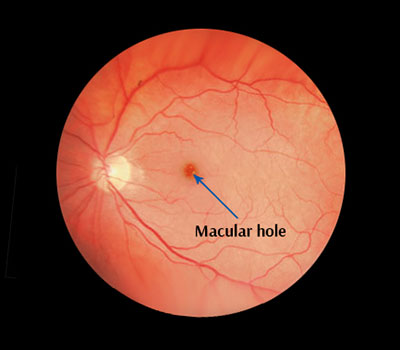
It is a small defect in the centre of the retina at the back of the eye. The hole may develop from abnormal traction between the retina and the vitreous, or it may follow an injury to the eye.
h. Retinal Detachment
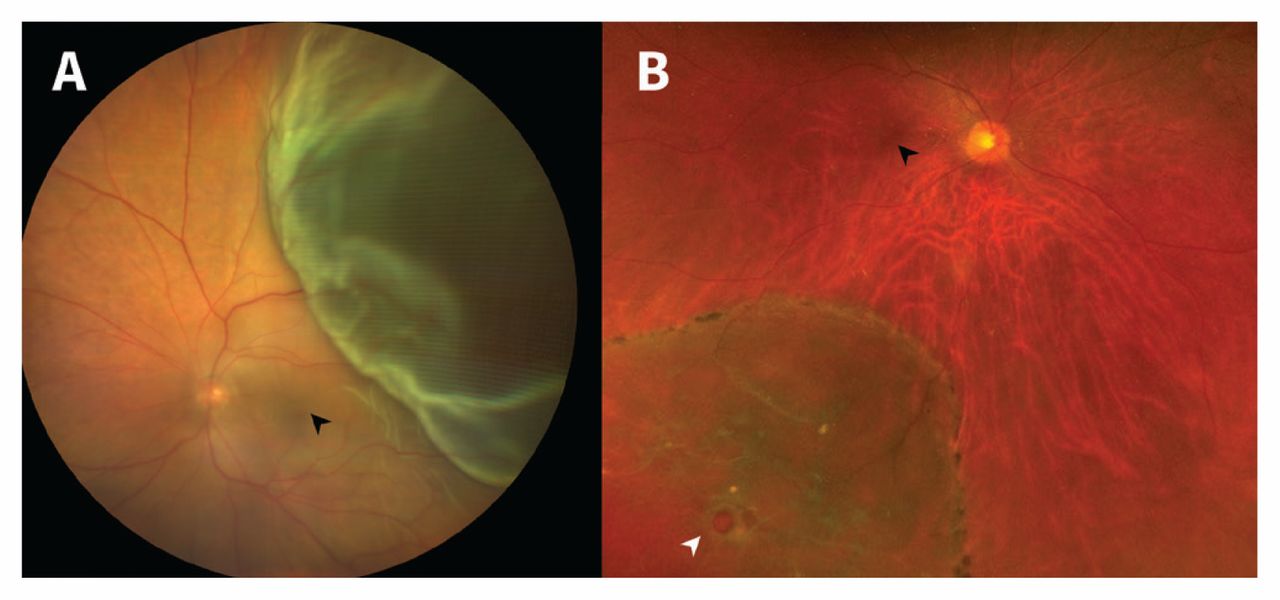
It is an eye emergency in which the retina is pulled away from its normal position at the back of the eye. The longer retinal detachment goes untreated, the greater your risk of permanent vision loss in the affected eye.
Symptoms of Retinal diseases
Many retinal diseases share some common signs and symptoms. These may include:
- Seeing floating specks or cobwebs
- Seeing flashes of light
- Seeing a central black spot
- Blurred or distorted (straight lines look wavy) vision
- Defects in peripheral vision
- Loss of vision
Risk factors – These include:
- Having diabetes, hypertension or other diseases
- Aging
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Eye injury
- Family history of retinal diseases
- Stress
When should I see a doctor?
It is important to pay attention to any changes in your vision and find care quickly. Seek immediate medical attention if you suddenly have floaters, flashes, or reduced vision. These are warning signs of potentially serious retinal disease.
Importance of a routine eye examination
It is essential to keep your retina functioning properly to enjoy a lifetime of good eyesight. Many retina problems can be detected by your eye doctor before you notice any significant symptoms.
Routine eye exams enable your eye doctor to examine your eyes for signs of serious retina problems so treatment can be instituted early.
Services available at Zamindar Microsurgical Eye Centre
We have a dedicated retina clinic where screening, early detection, treatment and systematic follow-up of patients is done.
We have the following diagnostic tools:
a. Fundus photography
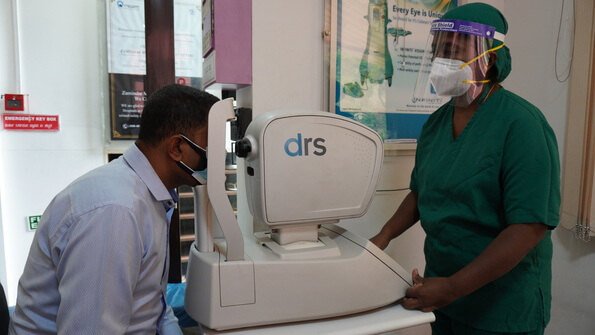
Our DRS (Digital Retinography System) is a fully automated fundus camera that provides high quality retinal images. These can be used by your doctor to explain your eye condition to you. It also helps as an objective way of comparing images to highlight the course of the disease process.
b. Primus 200 OCT
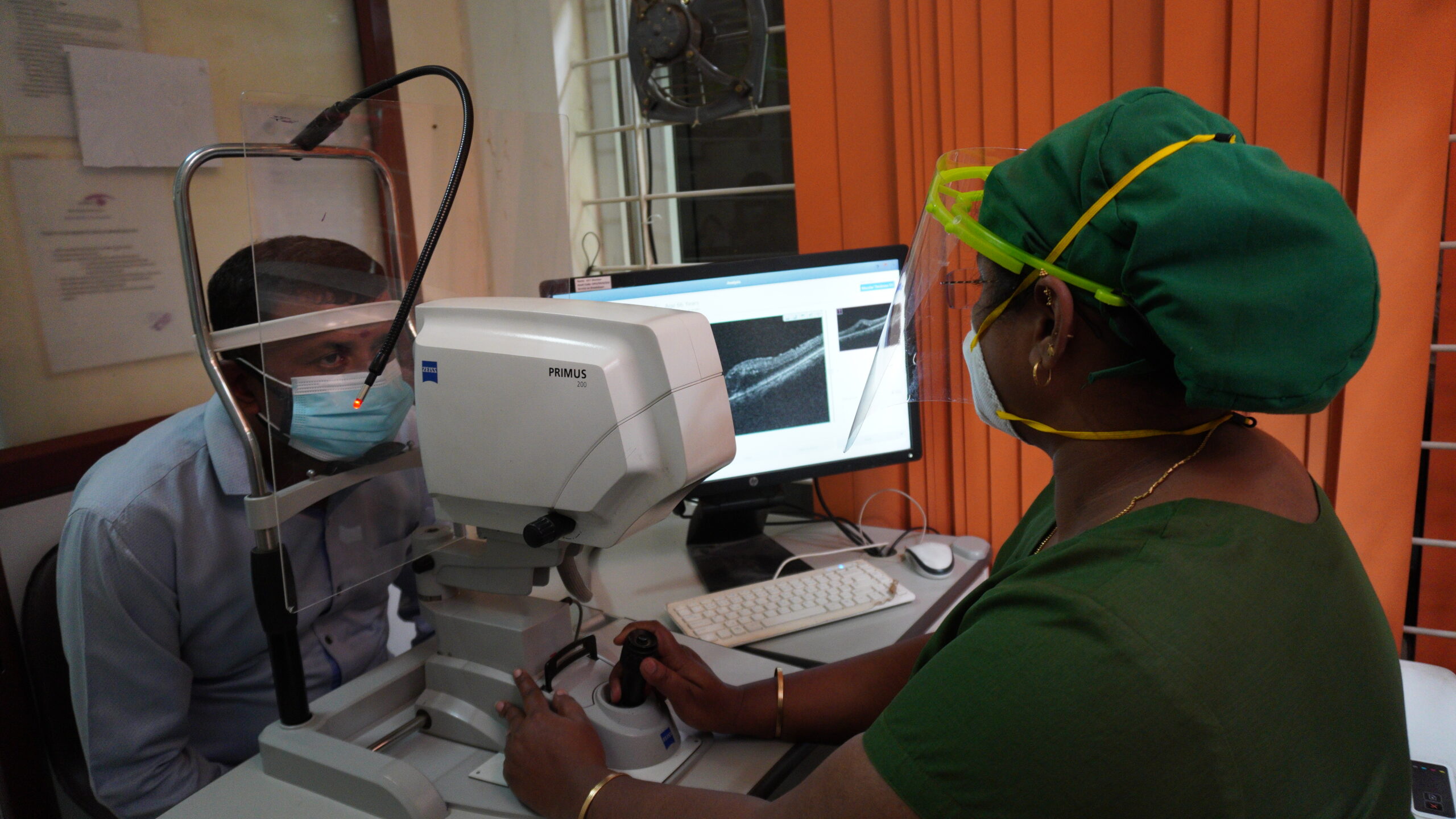

Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a valuable tool in detecting and quantifying retinal pathology. OCT uses light waves slicing through tissue layers at the back of the eye to produce high-resolution cross-sectional images of the retina, macula and optic nerve.
Treatment Protocol followed at Zamindar Microsurgical Eye Centre
Depending on the condition, treatment goals may be to stop or slow the disease and preserve, improve, or restore vision. Untreated, some retinal diseases can cause severe vision loss or even blindness.
a. LASER photocoagulation
This is done to reduce the risk of vision loss caused by diabetic retinopathy. Laser is used to destroy abnormal blood vessels and preserve central vision. This treatment stabilises the progression of diabetic retinopathy and prevents future vision loss.
b. Intra-Vitreal injection
It is the method of administration of drugs into the eye by injection with a fine needle. It is used to treat various eye diseases, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), diabetic retinopathy, venous occlusion and infections inside the eye. This procedure ensures a more localised delivery of medications to the targeted site. It is performed in the operation theatre under strict aseptic precautions.
We offer a variety of intravitreal injection options to our patients.
Know More About Retina From Experts
Adverse effects of Diabetes on eyes! – Dr Samina F Zamindar
Diabetic Retinopathy and Diabetes Related Eye Problems by Dr. Suma Krishnan | Zamindar Eye center
To Get The Best Eye Treatment At The
Top Eye Hospital In Bangalore
|
Call for an appointment! |
|
Opt for
|

